Page 23 - needle bearings
P. 23
Load Rating and Life
NTN
"Basic static load rating" is defined as such a constant
2.10 Radial internal clearance, surface static load that results in permanent deformation of the
roughness and surface hardness, and said limit value, which is then expressed in net radial load
bearing life for radial bearings and in net axial load for thrust
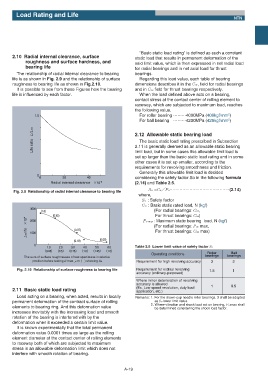
The relationship of radial internal clearance to bearing bearings.
life is as shown in Fig. 2.9 and the relationship of surface Regarding this load value, each table of bearing
roughness to bearing life as shown in Fig.2.10. dimensions describes it in the Cor, field for radial bearings
It is possible to see from these Figures how the bearing and in Coa field for thrust bearings respectively.
life is influenced by each factor. When the load defined above acts on a bearing,
contact stress at the contact center of rolling element to
raceway, which are subjected to maximum load, reaches
the following value.
2
1.0 For roller bearing ⋯⋯⋯4000MPa (408kgf/mm )
2
For ball bearing ⋯⋯⋯4200MPa (428kgf/mm )
Life ratioɹL L 2.12 Allowable static bearing load
The basic static load rating prescribed in Subsection
2.11 is generally deemed as an allowable static bearing
limit load, but in some cases this allowable limit load is
set up larger than the basic static load rating and in some
other cases it is set up smaller, according to the
requirements for revolving smoothness and friction.
Generally this allowable limit load is decided
0
0 20 40 considering the safety factor So in the following formula
Radial internal clearanceɹʷ10 -3 (2.14) and Table 2.5.
So CoʗPoʜʜʜʜʜʜʜʜʜʜʜʜʜʜ(2.14)
Fig. 2.9 Relationship of radial internal clearance to bearing life
where,
So : Safety factor
Co : Basic static rated load, N (kgf)
3000
(1.0) (For radial bearings: Cor,
(0.85) For thrust bearings: Coa)
L10 lifeɹʷ10 4 1000 (0.37) Po max : Maximum static bearing load, N (kgf)
2000
(For radial bearings: Por max,
For thrust bearings: Coa max)
(0.09)
(0.18)
0
1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 6.0 Table 2.5 Lower limit value of safety factor S0
ʢ0.25ʣ ʢ0.5ʣ ʢ0.75ʣ ʢ1.0ʣ ʢ1.25ʣ ʢ1.5ʣ
Operating conditions Roller Ball
The sum of surface roughnesses of test specimens in relative bearings bearings
position before testing R max Жm ( ) showing Ra Requirement for high revolving accuracy 3 2
Fig. 2.10 Relationship of surface roughness to bearing life Requirement for ordinal revolving 1.5 1
accuracy (ordinary-purposed)
Where minor deterioration of revolving
accuracy is allowed 1 0.5
(Ex. Low speed revolution, duty load
2.11 Basic static load rating application, etc.)
Load acting on a bearing, when acted, results in locally Remarks: 1. For the drawn-cup needle roller bearings, 3 shall be adopted
permanent deformation of the contract surface of rolling as So lower limit value.
2. Where vibration and shock load act on bearing, Po max shall
elements to bearing ring. And this deformation value be determined considering the shock load factor.
increases inevitably with the increasing load and smooth
rotation of the bearing is interfered with by the
deformation when it exceeded a certain limit value.
It is known experimentally that the total permanent
deformation value 0.0001 times as large as the rolling
element diameter at the contact center of rolling elements
to raceway both of which are subjected to maximum
stress is an allowable deformation limit which does not
interfere with smooth rotation of bearing.
A-19